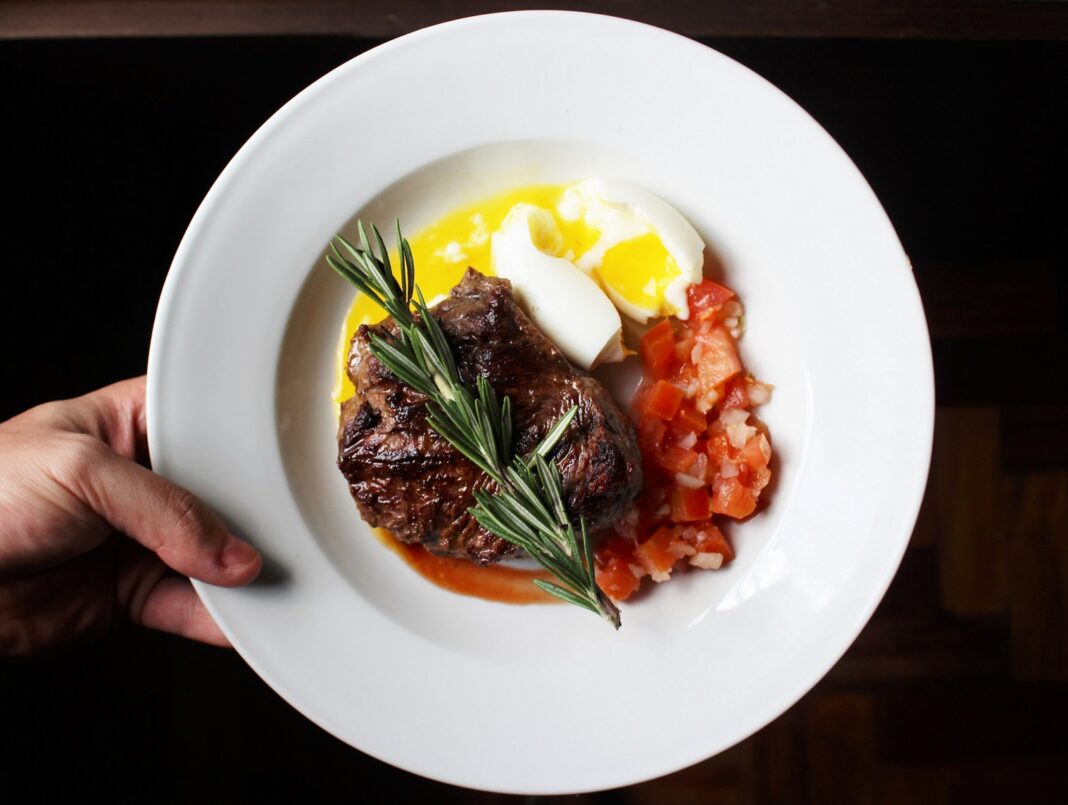
Unsplash: Eduardo Roda Lopes
What are the best protein sources? Protein is an essential macronutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including muscle repair and growth, immune function, and hormone production. Including high-quality protein sources in your diet is crucial to gaining muscle and strength and maintaining overall health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into the topic and explore in detail some of the best sources of protein, both from animal and plant-based foods, supported by scientific research.
BEST SOURCE OF PROTEIN #1: MEAT
Lean meats such as chicken breast, turkey, lean beef, and pork tenderloin are widely recognized as excellent sources of protein. In addition to their high protein content, these meats provide all essential amino acids, vitamins (such as B vitamins), and minerals (such as iron and zinc). Including lean meats in your diet can contribute to the overall protein intake while offering valuable nutrients that support muscle growth and optimal health.
BEST SOURCE OF PROTEIN #2: FISH AND SEAFOOD
Fish, including varieties such as salmon, tuna, trout, and sardines, are not only rich in protein but also offer the added benefit of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are healthy fats that have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease and improved brain health. Incorporating fish and seafood into your diet provides a dual advantage of protein and essential nutrients.
See also: Healthiest Sushi Choices
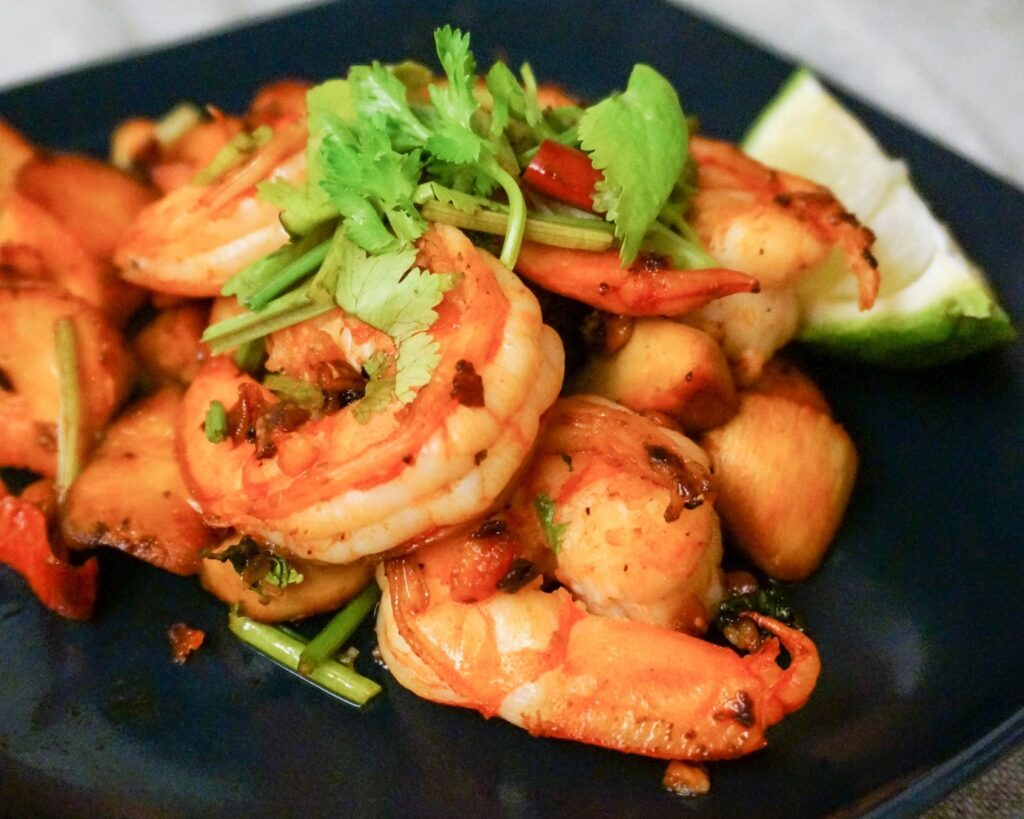

BEST SOURCE OF PROTEIN #3: EGGS
Eggs are a versatile source of protein, suitable for various culinary applications. They are complete protein sources, containing all nine essential amino acids necessary for the body. Additionally, eggs are packed with nutrients such as vitamins A, D, E, and B12, as well as choline and selenium, which further contribute to their nutritional value.
See also: Egg White vs. Whole Egg
BEST SOURCE OF PROTEIN #4: DAIRY
Dairy products, including milk, cheese, yogurt, and others, are well-known sources of protein. Greek yogurt, in particular, stands out for its high protein and lower sugar content. Apart from protein, dairy products provide essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and other important vitamins and minerals that support bone health and overall well-being.
BEST SOURCE OF PROTEIN #5: LEGUMES
Legumes, encompassing a variety of beans, lentils, chickpeas, and more, are excellent plant-based protein sources. They not only offer a substantial amount of protein but also provide dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Legumes are a valuable addition to vegetarian and vegan diets as they offer a diverse range of nutrients necessary for a balanced diet.
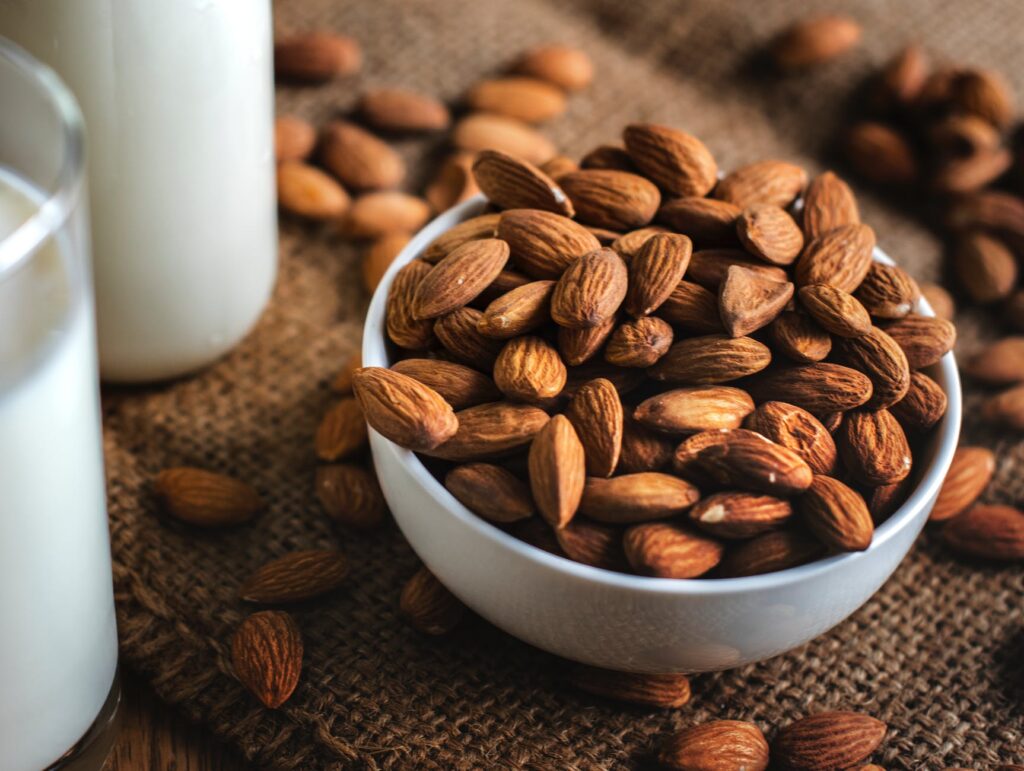
BEST SOURCE OF PROTEIN #6: NUTS AND SEEDS
Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, peanuts, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and hemp seeds, are not only rich sources of protein but also contain healthy fats. They are packed with nutrients such as vitamin E, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids. Including a variety of nuts and seeds in your diet can provide an array of health benefits.

BEST SOURCE OF PROTEIN #7: SOY
Soy-based products like tofu, tempeh, edamame, and others, serve as excellent sources of protein for vegetarians and vegans. Soy protein is considered a high-quality plant protein, as it contains all the essential amino acids required by the body. These soy products offer versatility in cooking and can be incorporated into various dishes to enhance protein intake.
BEST SOURCE OF PROTEIN CONCLUSION
Including protein-rich foods in your diet is crucial for gaining muscle and strength and maintaining optimal health. The best sources of protein include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, seeds, and soy products. By incorporating a variety of these protein sources into your meals, you can ensure you’re getting all the essential amino acids and other vital nutrients your body needs for overall well-being.
Sources:
Kris-Etherton PM, et al. The role of meat in strategies to achieve a healthy, sustainable diet rich in plant foods: A review. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019;111(3):666-680.
Mozaffarian D, Rimm EB. Fish intake, contaminants, and human health: Evaluating the risks and the benefits. JAMA. 2006;296(15):1885-1899.
Ruxton CH, Derbyshire EJ, Gibson S. The nutritional properties and health benefits of eggs. Nutr Food Sci. 2010;40(3):263-279.
Weaver CM, et al. Choosing foods for a healthy diet. J Nutr. 2013;143(3):557S-567S.
Ganesan K, et al. Comparative assessment of protein quality of some commonly consumed legumes in India. Food Chem. 2019;276:678-686.
Ros E. Health benefits of nut consumption. Nutrients. 2010;2(7):652-682.
Messina V. Soy and health update: Evaluation of the clinical and epidemiologic literature. Nutrients. 2016;8(12):754.
See also: How Much Protein for Muscle Growth?